Ionic or Electrovalent bond (properties,/characteristics, Definition,types,structures, examples)

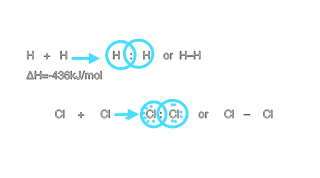
IONIC OR ELECTROVALENT BONDS: Definition of ionic or Electrovalent bond: It formed by electrostatic attraction between positive and negative ions, this is achieve by the transfer of single or more electrons to the atoms or atomic groups. • Atom loses or gain electrons to gain nearest Nobel gas configuration. • Ionic bonds are most likely to formed by when compounds have low ionization energies will react with elements have higher electronegative and electron affinity. • Generally: Group IA and IIA react with VI A or VII A. • Mostly metals and non metal react to form the ionic compounds. Reaction of sodium with chloride(example of electrovalent compounds): Na +Cl ---->NaCl In this reaction sodium loses a single electron to achieve neon ( Nobel gas) configuration. The energy it required is 496kJ/mol Where as the chlorine attain a electron and converted to chloride ion it is trying to get electronic configuration of argon . The energy it releases is 349kJ/mol IONIC CRYSTAL ST