Types of solids and properties of crystalline solids
Solids:
solids are substance s which has rigid, have definite shape and definite volume
Typeses of Solids:
There are three types of solid
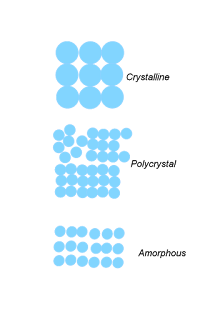
crystalline
polycrystalline
amorphous solids
crystalline Solids:
This is the substance in which molecules and atoms have a definite shape, arrangeed in definite three dimensional manner.
whole volume -periodic
NaCl
Amorphous solids.
this re the solids in which molecules and atoms ,ions do not have regular arrangement.
example of amorphous solids:
rubber, plastic, glue, glass.
Many crystalline solids converted to amorphous solids by cooling them rapidly after melting.
amorphous solids do not have sharp melting points.they have small range of regularity but large range of orderly arrangement in amorphous solids do not exist
non periodic
poly crystalline:
composed of many crystallite of varying shape and orientation.
each grain -periodic
Properties/characteristics of crystalline solids.
Melting points:
crystalline can be identified by their sharp melting points.
cleavage planes:
whenever crystalline solids broken down they do so along definit planes called cleavage planes.
Anisotropy
Depending on the direction some crytstals show variation in physical properties.
such properties called anisotropic properties and phenomenon known as anisotropy.
refractive index, coefficient of thermal expansion, thermal and electrical Conductivity are also sometimes anisotropic in natureof some Crystals.
Example:
graphite electrical Conductivity is different in one direction them othet.
symmetry
When crystal is rotated by 360° along its axis the repetition of faces, angles or edges is called symmetry.
Isomorphism:
Two crystalline substance exist insome crystalline form.
this substances are called ismorphs of each other.depemd upon number of atoms their way of combination not on the chemical nature of atoms On different compounds ratio of atoms is such that isomorphism is possible but their chemical properties are different.
Example Zn, cd
crystalline form: hexagonal
atomic ratio:. 1:1
Habitat of crystal.
when saturated solution is cooled or low cooling of the liquid crystal take place crystals are obtained.
the shaoe in which crystal usually grows is the habitat of crystal s.
polymorphism:
when one compund exist in more then one form. this compound is known as polymorphic snd phenomenon is called polymorphism.
this have different chemical properties but sam chemical properties.
Transition of temperature:
this is the temperature at which the two crystalline form of a compound exist in equilibrium with each other. at this temperature one crystalline form of substance changes to another form.
Allotropy:
the element thaexistsst in more than one crystalline form is known as allotropy and the element is called allotropic forms or allotropes.
Examples:
Sulfur
crystalline form: rhombic, monoclinic
Questions:
Cleavage of crystal s is itself anisotropic behavior.
what is the habitat of a crystal?
Difference between amorphous, crystalline, polycrystalline solids.

Comments
Post a Comment