Covalent Bond (Polar and non polar types, examples)
Covalent Bond:
Definition:
covalent Bond is form by the mutual sharing of electrons between two atoms.
Each atom contributes one electron from its valence electron shell to the shared pair of electrons.
According to lewis ,paring of electrons should lead to nobel gas configuration.the mutual sharing of elecrrons pair is is considered to be possesed by boththe atoms in common,which will contributes to the electronic configuration of each atom of the molecule.
in a covalent Bond sharing of electron pair is energetically favourable energy is liberated when two atoms form a covalent bond. Shared pair of electrons lie between nuclei of two atoms so electron attracted by two nuclei.where as electron repel each other as well as electroms also repel each other. The repulsion is offset by attraction of electron and nuclei. Nuclei shared electron pair is held together by this net attractive forces.
Lewis Structure:
shared electron pair is represented by the dot or line.Lewis structure use only dot whereas modern structure also use line for shared electron pair
Same or low Electronegativity:
covalent bond is fom by atoms which have same or low electronegativity
Reaction between two non-metal cause formation of covalent Bond.
Examples of covalent Bond:
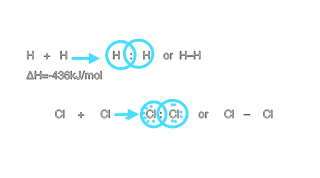
Hydrogen have two atoms which have one electron in valence shell.hydrogen share this electron and aquire stable helium configuration and hydrogen became stable.
Cl2 have seven Valence electron. Each share one electronic and achieve stable octet Cl2 aquire stable electron configuration of argon (nobel gas).
In Cl2 atoms not electron pair are involve in bonding.This Electrons are Called non-bonding, lone pair electrons, unshared electron pair.
Certain atoms(C, O, N) share more then one electron atom to achieve octet
Two atoms form :
Single Covalent Bond: share one electron pair
Double covalent bond: share two electron pair
Triple covalent Bond: share three electron pair.
Dot formula
Types of covalent Bond:
Non-polar Covalent bond
Polar covalent Bond
Non polar:
Electron pair is shared equally between two nuclei.
Equally shared two identical atoms having same Electronegativities.
H-H, Cl-Cl
Even charged these are Electrically neutral.
Electron density is symmetrical About the plane that is perpendicular to a line about the two nuclei.
Non polar compounds : homo nucoear diatomic molecules, binary compounds of non metals, and most compund of hydrogen and carbon
Polar covalent Bond:
The electrin pair is shared unequally and the bonded atoms aquire a partial negative and positive charge
Covalent Bond form between two non identical atoms.
Examples of polar :
H-Cl, H-Br
Greater the electronegativity difference, greater tge polarity.
A molecule have partial negative or positive charge separated by the distance is considered as the dipoles(two poles).
For polar bond:
At least One polar bond or lone pair of electrons should be present on central atom.
if more then one polar bond is present then, this bond should not be arranged symmetrical that there bond polarities cancel.
For Example:
Water molecule is angular.
Have two pair of lone pair of electrons on oxygen atoms.
water dipoles are directed from H to O (oxygen is more electronegative then Hydrogen).
these reinforced by strong dipoles associated with the two lone pair on the oxygen atoms. Due to which water molecules are very polar.
Beryllium chloride is linear
Each Be-Cl molecule is polar but the bond dipoles are same in magnitude and are opposite in directions, So they cancel to give non polar molecule
Boron triflouride:Boron triflouride is trigonal planar.
It has polar bond but molecule is non polar
three bond moment are of equall magnitude Because of the symmetry of the molecule bond moments are cancel.they point to the corners of equilateral triangle.
distinguish between ionic and covalent bonds.




Comments
Post a Comment